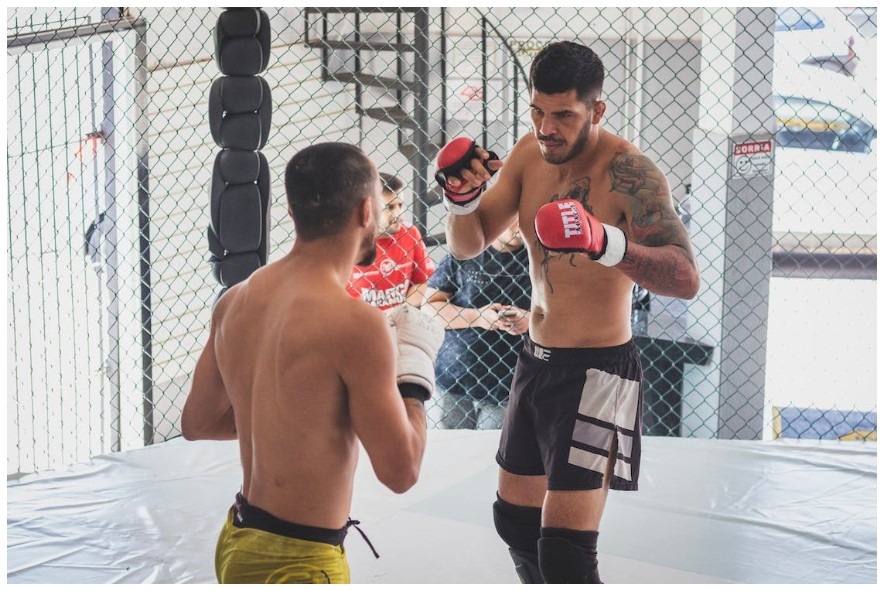
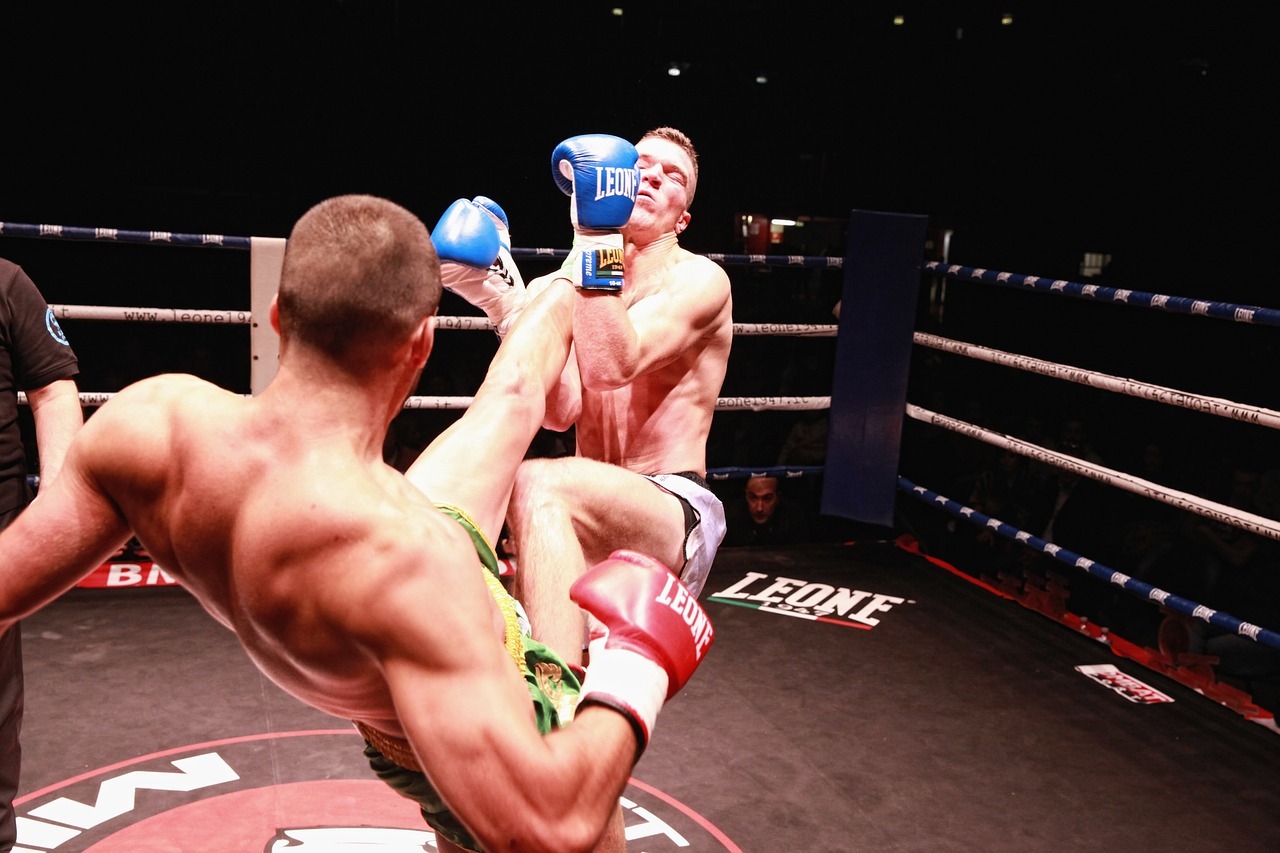
Mixed Martial Arts (MMA) is a full-contact combat sport that has surged in popularity globally, captivating audiences with its blend of techniques and disciplines. This article delves into the world of MMA, exploring its history, rules, styles, training, notable organizations, and its impact on popular culture.
The Origins and Evolution of MMA
MMA’s roots can be traced back to various combat practices across the world, but its modern form started taking shape in the late 20th century. The sport gained prominence with the advent of the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) in 1993 in the United States. Initially aimed at finding the most effective martial arts for real unarmed combat situations, it evolved to incorporate elements from various disciplines, creating a unique sport.
Here’s a short overview of some of the most well-known MMA fighters:
- Conor McGregor: An Irish fighter known for his striking skills and charismatic personality. McGregor became the first UFC fighter to hold titles in two weight classes simultaneously and is known for some of the highest-grossing pay-per-view (PPV) events in MMA history.
- Anderson Silva: Hailing from Brazil, Silva is considered one of the greatest MMA fighters of all time. He holds the record for the longest title reign in UFC history at 2,457 days and is known for his striking accuracy and defensive prowess.
- Georges St-Pierre (GSP): A Canadian fighter renowned for his well-rounded skill set. GSP was a dominant welterweight champion and also won the middleweight title, becoming one of the few multi-division champions in UFC history.
- Jon Jones: An American fighter known for his exceptional talent and reach advantage. Jones is considered one of the best pound-for-pound fighters in the world and has held the UFC Light Heavyweight Championship multiple times.
- Ronda Rousey: An American fighter who became the first woman to sign with the UFC. Rousey was the inaugural UFC Women’s Bantamweight Champion and is known for her judo background and quick submission victories.
- Khabib Nurmagomedov: Hailing from Russia, Khabib is celebrated for his grappling skills and undefeated record in his career. He retired as the UFC Lightweight Champion and is known for his dominant performances inside the octagon.
- Amanda Nunes: A Brazilian fighter considered the best female MMA fighter of all time. Nunes is the first woman to become a UFC two-division champion and has victories over some of the biggest names in women’s MMA.
- Fedor Emelianenko: A Russian heavyweight fighter, widely regarded as one of the greatest MMA fighters of all time. Known for his time in Pride FC, Fedor has notable victories over several top fighters and is celebrated for his striking and ground game.
- Chuck Liddell: An American fighter known for his knockout power. Liddell was a popular UFC Light Heavyweight Champion and played a significant role in bringing MMA into the mainstream.
- Demetrious Johnson: An American fighter, known for his agility and technique. Johnson held the UFC Flyweight Championship for nearly six years and defended his title a record 11 times.
Each of these fighters has contributed to the evolution and popularity of MMA, showcasing a blend of skill, determination, and unique fighting styles that have made the sport what it is today.
The Fusion of Fighting Styles
MMA stands out due to its synthesis of various martial arts. Fighters often combine techniques from Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu, Muay Thai, Boxing, Wrestling, Judo, and Karate, among others. This blend allows for a diverse range of fighting tactics, including striking, grappling, and ground fighting.
Rules and Regulations
MMA has a set of standardized rules known as the Unified Rules of Mixed Martial Arts. These include weight classes, round durations, and a list of legal and illegal moves. Safety gear such as gloves is mandatory. Matches can end via knockout, submission, judge’s decision, or technical knockout, ensuring a definitive outcome. These rules have been established to ensure fighter safety and to provide a clear framework for competition. Some of the key rules and regulations include:
- Weight Classes: MMA fighters compete in specific weight classes to ensure fair and balanced matches. These classes range from Flyweight (up to 125 pounds) to Heavyweight (over 205 pounds, up to 265 pounds).
- Rounds and Time Limits: Non-title bouts typically consist of three five-minute rounds, while championship fights are usually five five-minute rounds. There is a one-minute rest period between rounds.
- Apparel and Equipment: Fighters are required to wear MMA gloves that are smaller and lighter than traditional boxing gloves. They also wear shorts without pockets, and no shoes. Additional protective gear like mouthguards and groin protectors is mandatory.
- Fighting Techniques: MMA allows a wide range of fighting techniques from various martial arts disciplines, including striking (like punches and kicks), grappling (like clinch holds and takedowns), and ground fighting (like submission holds).
- Legal and Illegal Moves: Certain techniques are prohibited to maintain fighter safety. These include strikes to the back of the head and spine, eye gouging, biting, hair pulling, throat strikes, and intentional throwing of an opponent out of the ring or fenced area.
- Winning the Fight: Matches can be won in several ways, including knockout (KO), technical knockout (TKO), submission (when a fighter taps out or verbally submits), judge’s decision (based on scoring the fight), or disqualification of an opponent.
- Scoring System: If a fight goes the distance, it is scored by judges. Scoring is based on effective striking and grappling, control of the fighting area, effective aggressiveness, and defense.
- Fouls and Violations: Committing fouls can result in point deductions and, in severe cases, disqualification. Fouls include but are not limited to head butting, eye poking, biting, hair pulling, and strikes to the groin.
- Medical Suspensions: To protect fighters, medical suspensions are often enforced after a bout, especially if a fighter suffers a knockout or significant injury. This suspension period prohibits fighters from competing for a specified duration to ensure proper recovery.
- Drug Testing: Most MMA organizations conduct drug testing to screen for performance-enhancing drugs and substances of abuse, adhering to anti-doping policies.
Training and Conditioning
Training for MMA is rigorous and multifaceted, focusing on building strength, endurance, flexibility, and technique. Fighters train in various disciplines, learning to strike and defend, grapple, and fight on the ground. Nutrition and mental conditioning are also integral parts of a fighter’s regimen.
Prominent Organizations
The UFC is the most renowned MMA organization globally, but others like Bellator MMA, ONE Championship, and the Professional Fighters League also host high-level competitions. These organizations have been instrumental in promoting the sport and attracting a global audience.
The Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) has a fascinating history that marks its evolution from a controversial no-holds-barred tournament to a globally recognized mixed martial arts (MMA) organization.
Early Years: The Beginning (1993-1997)
- Founding (1993): UFC was created by Art Davie, Rorion Gracie, and others. The first event, UFC 1, was held in Denver, Colorado, in 1993. It was intended to identify the most effective martial art in a real fight situation, featuring fighters from various disciplines.
- No-Holds-Barred Format: Initially, UFC had minimal rules, no weight classes, and was marketed with the tagline “There are no rules!” This format led to criticism due to its violent nature.
Growing Pains and Regulation (1997-2001)
- Introduction of Rules: Facing increasing scrutiny and pressure from lawmakers, UFC began to implement more rules, introducing weight classes, time limits, and a list of illegal moves to increase safety.
- Zuffa Era Begins (2001): In 2001, the UFC was purchased by Zuffa, LLC, led by Dana White and the Fertitta brothers. This change in ownership marked the beginning of a new era.
Mainstream Acceptance and Expansion (2001-Present)
- Regulation and Sanctioning: UFC worked towards gaining sanctioning from athletic commissions. The adoption of the Unified Rules of Mixed Martial Arts was crucial in legitimizing the sport.
- Television and Global Expansion: The launch of the reality TV show “The Ultimate Fighter” in 2005 on Spike TV significantly boosted the UFC’s popularity. The organization expanded globally, holding events worldwide.
- Rise of Superstars: Fighters like Chuck Liddell, Anderson Silva, Ronda Rousey, and Conor McGregor became household names, elevating the sport’s profile.
- Increased Competition and Women’s Division: The introduction of women’s divisions, notably with Rousey’s debut, further increased its appeal. UFC also faced competition from other MMA organizations, driving growth and innovation.
- ESPN Deal and Continued Growth: The UFC’s deal with ESPN in 2019 marked a significant milestone, further establishing it as a mainstream sport.
Impact on Popular Culture
MMA’s rise has significantly influenced popular culture. It’s featured in movies, television shows, and video games, and has also impacted the fitness industry, with MMA-style training becoming popular in gyms worldwide. Fighters like Conor McGregor and Ronda Rousey have become household names, transcending the sport.
Safety and Controversies
While MMA is a regulated sport, it’s not without risks. Concerns over fighter safety, weight cutting practices, and the long-term health impacts are ongoing. Regulatory bodies continuously work to ensure fighter safety and fair play.
The Future of MMA
MMA continues to evolve, with an increasing focus on technical skill and strategic fighting. Its growing popularity, especially among younger audiences, suggests a bright future, with potential developments in rules, training methods, and global reach.
Conclusion
MMA is more than just a sport; it’s a dynamic and evolving spectacle of human endurance, skill, and strategy. Whether as a participant or a spectator, engaging with MMA offers an insight into the complexities and richness of this modern combat sport, reflecting a diverse tapestry of martial arts traditions from around the world.